QL LANDSCAPE
The Landscape Application provides utilities which assist the landscape architect to add site features, plants, surface treatments and irrigation to a landscape plan, and product estimates and reports of costs.
It also provides tools for composite site analysis for such attributes as slope, aspect, height and proximity to major features. The ever increasing focus on the environment has escalated the need for an application that enables the efficient landscaping and cost management of the built environment.
The ever increasing focus on the environment has escalated the need for an application that enables the efficient landscaping and cost management of the built environment. Most importantly, this application enable cost estimates and visualisation of the landscape would costs, years after practical completion.
Most importantly, this application enable cost estimates and visualisation of the landscape would costs, years after practical completion.
The Landscape Application provides utilities which assist the
landscape architect to add site features, plants, surface treatments and irrigation to a landscape plan, and produce estimates and reports of costs. It also provides tools for Composite Site Analysis for such attributes as
slope, aspect, height and proximity to major features.
Landscape assigns a number of different layers on which to place the different design elements. These layers can be fully customised by the user to suit a particular file management system, or can be used without file management. As graphic models are built up using Landscape, attribute data used
to describe and cost the project is stored in a database. To relate all the parts of a design, the database keeps them all as part of a Landscape Task.
As graphic models are built up using Landscape, attribute data used
to describe and cost the project is stored in a database. To relate all the parts of a design, the database keeps them all as part of a Landscape Task.
SYMBOLS
Adding Features And Furniture
The symbol placement macro places features at the actual height of
the ground at the x-y location defined by the cursor. It carries this out by referring to the digital terrain model of the site (loaded on a pre-defined layer). Some special symbols have been created for Landscape, and are accessed from the SYMBOLS icon. Users can also add their own symbols to the symbol database.
Some special symbols have been created for Landscape, and are accessed from the SYMBOLS icon. Users can also add their own symbols to the symbol database.
PLANTS
Plant Selection
To place plants in the drawing, Plant Selection Lists are used.
Some of these lists will have already been created for you, but in general you will create lists of commonly-used plants for particular purposes. You may give the list any name you like, and your own lists will be stored under the menu
Favourite Lists. To create plant selection lists, Sieves are used. The sieve is a process of selecting plants by nominating the characteristics you require the plant to have. You can also search for a
plant by providing all or part of its Latin or common name. Plants are stored in a relational database according to their genus
and species, together with their common names and a number of characteristics, such as origin, shape, foliage colour etc.
Plants are stored in a relational database according to their genus
and species, together with their common names and a number of characteristics, such as origin, shape, foliage colour etc.
Placing Plants
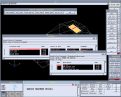 Plants are automatically placed on the digital terrain model at the
level of the surface. The graphic symbols which represent each plant are created using the usual AES facilities. The program attaches a colour to the bark, foliage and flowers, derived from descriptions in
the plant database. The graphics will also be modified according to the age of the plant, under the Growth Simulation facility.
Plants are automatically placed on the digital terrain model at the
level of the surface. The graphic symbols which represent each plant are created using the usual AES facilities. The program attaches a colour to the bark, foliage and flowers, derived from descriptions in
the plant database. The graphics will also be modified according to the age of the plant, under the Growth Simulation facility.
SURFACE TREATMENTS
Surface Treatments fall into four categories: Grassing, Planting areas, Pavements, Other treatments, indicated by different hatch patterns. The hatch pattern is linked to a database for costing purposes.
Placing Surface Treatments
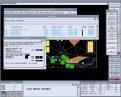 Treatments are selected from a list, and a form opens with default values for cost, display attributes, and other user-definable attributes, such as fertiliser requirements. The selected treatment can then be
applied to parts of the digital terrain model.
Treatments are selected from a list, and a form opens with default values for cost, display attributes, and other user-definable attributes, such as fertiliser requirements. The selected treatment can then be
applied to parts of the digital terrain model.
IRRIGATION
Adding Sprinklers
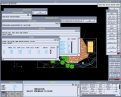 Sprinklers have symbols which are linked to a cost and attribute database. Information about the sprinklers is automatically inserted
in the database as they are added to the model. Sprinklers are organised according to manufacturer, model and nozzle configuration (full circle, half circle etc). Required precipitation rate can be
matched with the sprinkler spacing, based on available pressure. Sprinklers are displayed on the screen with circles to indicate coverage.
Sprinklers have symbols which are linked to a cost and attribute database. Information about the sprinklers is automatically inserted
in the database as they are added to the model. Sprinklers are organised according to manufacturer, model and nozzle configuration (full circle, half circle etc). Required precipitation rate can be
matched with the sprinkler spacing, based on available pressure. Sprinklers are displayed on the screen with circles to indicate coverage.
Placing Sprinkler Pipes
Pipes can be placed using nominal
sizes, which can then be sized by measuring the flow. The pipes will be annotated with their required sizes, and this information inserted in the database.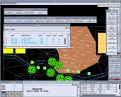 Landscape provides two ways to design pipework to serve sprinklers: using AES Pipes, and using a simplified method (remaining within AES Model).
Landscape provides two ways to design pipework to serve sprinklers: using AES Pipes, and using a simplified method (remaining within AES Model).
COST ESTIMATION
Estimation Of Costs
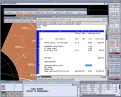 In the process of placing the various landscape items on the drawing
- plants and furniture symbols, treatment hatch patterns, pipes and sprinklers - the cost and quantity of those items has been entered in a database. Details of all landscape items in the current model are
stored in a Project List for each type of item.
In the process of placing the various landscape items on the drawing
- plants and furniture symbols, treatment hatch patterns, pipes and sprinklers - the cost and quantity of those items has been entered in a database. Details of all landscape items in the current model are
stored in a Project List for each type of item.
Reports
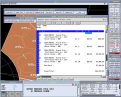 A Bill of Materials can be produced as a spreadsheet listing all
costed items, with quantities and rates. The Costing Module will summarise costs for all elements and provide a total cost for the project.
A Bill of Materials can be produced as a spreadsheet listing all
costed items, with quantities and rates. The Costing Module will summarise costs for all elements and provide a total cost for the project.
COMPOSITE SITE ANALYSIS
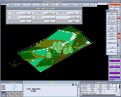 The Composite Site Analysis module of Landscape enables you to view a landscape in three dimensions and shade the digital terrain model according to the following criteria:
The Composite Site Analysis module of Landscape enables you to view a landscape in three dimensions and shade the digital terrain model according to the following criteria:
|
A square grid, or mesh, is imposed over the landscape following the profile of the digital
terrain model. The fineness of the grid can be chosen according to the accuracy required, and the speed at which you wish the analysis to be carried out.
The user can specify colours to be used for different functions and ranges of attributes, and can specify the true north angle and latitude of the site.
Products
To contact Quantum Leap - email:
info@qleap.net
Copyright © 2001 Quantum Leap Consultancy (Australia) ALL RIGHTS RESERVED

HOME | introduction | company profile | solutions | partners | clients | news